No.190 May 28, 2022 |
| |
Subscribe |
 |
|
|
| |
Contact us |
 |
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| |
| Unitalen News |
|
| |
| Unitalen Insights |
|
| |
|
In this issue
|
 |
|
|
 China National Intellectual Property Administration Released the 2021 Annual Report China National Intellectual Property Administration Released the 2021 Annual Report
|

|
| |
| |
Recently, the CNIPA released the 2021 annual report, which involves the application of patents, trademarks, geographical indications, and layout designs of integrated circuits in 2021 as follows:
In 2021, the number of patent applications for invention in China was 1.586 million, a year-on-year increase of 5.9%. China's invention patent allowance rate was 55.0%. In 2021, a total of 73,000 international patent applications submitted via the PCT route were accepted, a year-on-year increase of 1.5%. In 2021, 107,000 PCT international applications entering the Chinese national phase were received, a year-on-year increase of 6.3%, including 106,000 invention patent applications and 916 utility model patent applications.
In 2021, the number of trademark registration applications in China was 9.451 million, including 9.193 million domestic trademark applications, accounting for 97.3% of the total, a year-on-year increase of 0.8%; and the number of foreign trademark applications in China was 258,000, accounting for 2.7% of the total, a year-on-year increase of 11.6%. In 2021, a total of 5,928 applications for the Madrid trademark international registration submitted by Chinese applicants were received.
In 2021, 22 applications for the protection of GI products were accepted, 99 GI products were approved for protection, and 7,677 market entities were approved to use special marks for GI products. By the end of 2021, a total of 215 foreign geographical indication trademarks had been approved for registration, an increase of 2.4% over the end of 2020. The top three countries are: France (154 cases), Italy (24 cases), and the United States (14 cases). The registrations from the three countries account for 89.3% of the foreign geographical indication trademark registrations in China.
In 2021, a total of 20,000 applications for registration of layout designs of integrated circuits were received, a year-on-year increase of 41.6%; and 13,000 were published and issued certificates, a year-on-year increase of 11.6%. Since the implementation of the Protection Regulation of Layout Designs of Integrated Circuits on October 1, 2001, a total of 66,000 cases for registration of layout-designs of integrated circuits have been received, and 52,000 of them have been published and issued certificates.
For details, please click: China National Intellectual Property Administration 2021 Annual Report
(Source: the CNIPA)
|
|
|
| |
| |
|
 Reminder on Handling Stamp Tax Related Business Reminder on Handling Stamp Tax Related Business
|

|
| |
| |
In order to comply with the implementation of the Stamp Tax Law of the People's Republic of China, the CNIPA will stop the collection of stamp taxes involving patent certificates and integrated circuit layout designs registration certificates from July 1, 2022 (inclusive).
In order to better protect the rights and interests of the right holders, for the overpaid, wrongly paid and double-paid stamp taxes within 3 years from the date of payment, the relevant right holders are requested to submit an observations (about the fees) as soon as possible to go through the refund procedures.
According to the relevant business processing procedures, the patent applications for registration after June 15, 2022 (inclusive) will be issued after July 1, 2022. Therefore, stamp tax is not required for registrations completed after June 15, 2022 (inclusive).
(Source: China Patent Electronic Application Website)
|
|
|
| |
| |
 Over One Hundred International Applications for Design Patents on the First Day of China's Entry to the Hague System Over One Hundred International Applications for Design Patents on the First Day of China's Entry to the Hague System
|

|
| |
| |
On May 5 Beijing Time, the Hague Agreement Concerning the International Registration of Industrial Designs (Hague Agreement) entered into force in China. On the effective day, a total of 49 Chinese enterprises submitted 108 international applications for design patents. The CNIPA received 58 international applications for design patents. As of 5:30 PM Geneva Time, the WIPO had received 50 international applications for design patents directly from Chinese applicants.
Lenovo (Beijing) Co., Ltd., GEMT Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. and Beijing Xiaomi Mobile Software Co., Ltd. etc. pace all applicants via the CNIPA route while WIPO's data suggests Shenzhen Smoore Technology, Dreame Innovation Technology and Shenzhen TCL Digital Technology are the most prolific Chinese filers.
(Source: the CNIPA Official WeChat Account)
|
|
|
| |
| |
 With over 1.6 Million 5G Base Stations, China Takes Global Lead in Number of Patents With over 1.6 Million 5G Base Stations, China Takes Global Lead in Number of Patents
|

|
| |
| |
According to the latest statistics from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People's Republic of China, by the end of April, China has built 1.615 million 5G base stations, becoming the first country in the world to build a 5G network on a scale based on an independent networking model, 5G base stations accounting for 16% of the total number of mobile base stations.
Since the issuance of 5G licenses in June 2019, China's basic telecom operators have adhered to the principle of overall planning and moderate advance, and promoted joint construction and sharing, so that 5G network construction can be faster and more efficient. According to the statistics, in 2021, 1.425 million 5G base stations had been opened in China, and the 5G network had covered all prefecture-level cities, more than 98% of county towns, and 80% of townships. The number of 5G mobile phone terminal connections reached 518 million. In the first quarter of this year, the number of newly constructed 5G base stations reached 134,000.
In recent years, China's 5G key technological innovation breakthroughs have made new progress. The number of 5G standard essential patents declared by Chinese companies remains the world leader.
(Source: People's Daily)
|
|
|
| |
| |
 The Ninth Formal Talks Between the CNIPA and the Swiss Federal Institute of Intellectual Property (IPI) and the Seventh Round Table of the Industry Community Held Online The Ninth Formal Talks Between the CNIPA and the Swiss Federal Institute of Intellectual Property (IPI) and the Seventh Round Table of the Industry Community Held Online
|

|
| |
| |
Recently, the CNIPA and the IPI held their ninth formal talks online. The principals of the CNIPA International Cooperation Department and the IPI International Trade Relations Department co-chaired the meeting as heads of delegations from both sides.
The two sides further conducted in-depth communication and discussions on the extension of patent term, standardization of trademark registration, promotion of innovation and development under the influence of the epidemic and incentive measures, geographical indication work, and IP international issues of common concern, etc. During the meeting, both offices also held the seventh China-Swiss Round Table of the Industry Community Online.
(Source: the CNIPA Official WeChat Account)
|
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cases in Spotlight
|
 |
| |
 Unitalen Assisted SunPure in Winning a Complete Victory in Patent Infringement Litigation and Invalidation Procedure Unitalen Assisted SunPure in Winning a Complete Victory in Patent Infringement Litigation and Invalidation Procedure
|

|
| |
|
|
Case Brief:
Founded in 2019, SunPure Technology Co., Ltd., is headquartered in Hefei National High-tech Industrial Development Zone, China. It is a high-tech innovative company focusing on research and development, production, sales and service of intelligent solar panel cleaning robots and standardized, specialized, and integrated cleaning solutions for Photovoltaic (PV) power plants.

Related products of SunPure
The patent involved is an invention patent applied for by Beijing Zhongdian Boson Intelligent Equipment Tech Co., Ltd. on March 6, 2020, with the patent number of 202020268065.5, and a title of "PHOTOVOLTAIC PANEL CLEANING ROBOT". In September 2021, the patentee filed a lawsuit with the Jinan Intermediate People's Court, claiming that the intelligent PV cleaning robot produced by the defendant SunPure Technology Co., Ltd. infringed the patent right thereof, and claimed economic losses and reasonable expenses of more than 1.18 million yuan. At the same time, Zhongdian Boson also listed cooperative enterprises of SunPure as co-defendants, which had a great impact on SunPure's normal business operations, promotion, and manufacturing activities.
Invalidation Procedure
After discussions with the client, Unitalen team decided to initiate the invalidation procedure while actively responding to the infringement lawsuit. On September 18, 2021, Unitalen filed an invalidation request regarding the right of the patent involved with the CNIPA for the first time, explicitly pointing out the grounds and evidences for invalidation that the patent involved did not possess novelty or involve an inventive step, and thus fails to comply with the conditions for granting a patent.
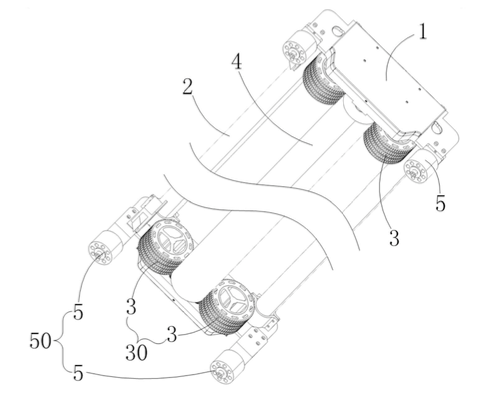
the Drawings of the patent involved
By carefully reviewing the application documents, authorization documents and the examination history documents during the authorization process of the patent involved, Unitalen team determined that the core inventive point of the patent involved is the positional relationship between the walking wheels and the hanging wheels, and parameters such as the wheel diameter and the center distance between the wheels of the photovoltaic panel cleaning robot, so as to improve the photovoltaic panel cleaning robot's ability to overcome obstacles between photovoltaic panels, such that the robot runs more smoothly between the photovoltaic panels. In combination with the evidence of the prior art and the analysis of infringement lawsuits, Unitalen team believed that the difficult point and the focus in the invalidation lies in the portion related to the parameter defining in the dependent claims of the patent involved. As a result, Unitalen team actively collected evidence from various aspects and formulated a comprehensive invalidation strategy. Based on the collection of various evidence and the full statements from multiple perspectives, the Invalidation and Reexamination Department finally adopted the claim of Unitalen team that the parameters defining in the dependent claims were a conventional selection.
The CNIPA deemed that the distinguishing technical features of the claims over the prior art belong to the conventional technical selection of those skilled in the art, and the technical effect thereof can be expected. Therefore, on April 2, 2022, the CNIPA made No. 54999 "Examination Decision on Request for Invalidation", declaring all the right of the patent involved invalid on the grounds that the patent involved lacks inventiveness.
Infringement Litigation Procedure
Regarding the infringement lawsuit brought by Zhongdian Boson with Jinan Intermediate People's Court against SunPure, Unitalen team immediately started the request for invalidation of the patent involved and applied to the CNIPA for expedited acceptance. After receiving the notice of acceptance of the invalidation request from the CNIPA, Unitalen team immediately requested the Jinan Intermediate People's Court to suspend the hearing of this case.
After determining the litigation strategy of the infringement lawsuit with the defense of the prior art as the breakthrough point, Unitalen team actively sought evidence that can be used to prove the relevant prior art, and such evidence can also assist the invalidation request procedure. After the efficient and thorough search of Unitalen team and SunPure, it was finally found that the photovoltaic panel cleaning robot equipped in a solar power station in an industrial park in Tianjin had been put into production in 2017 and the product was equipped with the same technical solution of the patent involved. Moreover, under the repeated communication between Unitalen team and the client and the unremitting efforts, finally a series of supporting material documents was obtained from the operator of the power station, forming a complete and solid chain of evidence to prove the facts.
With the assistance of SunPure, Unitalen team carefully planned for the evidence collection process, and proved from various perspectives that the technical solutions adopted by the patent involved had been disclosed by the products on the market long before the application date of the patent involved. Since the infringement lawsuit has not actually been tried in court, the evidence for publication of the product has not been confirmed by the trial court during the litigation process. However, it is certain that the solid evidence formed by Unitalen team has played a positive role in the invalidation process. Therefore, it is deemed that the technical solutions disclosed in the dependent claims of the patent involved belong to the common knowledge in the art.
In the end, after the CNIPA made the examination decision to declare all the rights of the patent involved invalid, Zhongdian Boson has lost the right basis to file a patent infringement lawsuit. On April 8, 2022, the Jinan Intermediate People's Court ruled to dismiss the plaintiff's lawsuit in accordance with the law, and Unitalen team represented the client winning the case.
Case Influence:
In this case, Unitalen Patent Litigation and Invalidation Team responded quickly and started the litigation and invalidation request procedures at the same time, which cooperated and guaranteed each other. Unitalen team actively searched and discussed repeatedly in the invalidation procedure to form a convincing evidence combination to initiate the invalidation procedure and finally succeeded. Meanwhile, Unitalen team actively promoted the case trial process, and resolved disputes efficiently and quickly only seven months after the other party filed the lawsuit to get rid of the burden of litigation for the client. The two-pronged approach of litigation and invalidation procedures not only won a comprehensive victory for the client, but also protected the client's commercial interests, protected its market operation and promotion, and eliminated the cloud of doubt.
|
|
|
| |
| |
 "CHOW LO FOOK Jewelry" Sued "Zhou Liu Fu Jewelry" for Infringement of Reputation Right and Discrediting due to the Alleging of "Fake Brand", and Zhou Liu Fu Jewelry Won a Series of Cases "CHOW LO FOOK Jewelry" Sued "Zhou Liu Fu Jewelry" for Infringement of Reputation Right and Discrediting due to the Alleging of "Fake Brand", and Zhou Liu Fu Jewelry Won a Series of Cases
|

|
| |
|
|
Case brief:
In July 2021, HK ZHOU LIU FU Gold Diamond Jewelry Group Co., Limited and HK CHOW LO FOOK Jewelry Int'l Group Limited ("ZHOU LIU FU Jewelry company" and "CHOW LO FOOK Jewelry") filed a counter-compensation against the malicious lawsuit and an unfair competition lawsuit against Zhou Liu Fu Jewelry Co., Ltd. ("Zhou Liu Fu Jewelry") with Shenzhen Luohu Court, arguing that Zhou Liu Fu Jeweler’s industrial and commercial complaints and multiple lawsuits with the people's courts in many places in the country against ZHOU LIU FU Jewelry company and its dealers belonged to malicious lawsuits, which also constituted unfair competition under Article 2 of the Law Against Unfair Competition. During the first-instance trial, after the two parties debated on the four elements of malicious lawsuit, the other party voluntarily gave up the counter-compensation against the malicious lawsuit, and only retained the cause of action for unfair competition lawsuit. Later, the two parties debated about "whether the prosecution behavior violated the principle of good faith and recognized business ethics". At the same time, after we pointed out that the other party's evidence had been altered in respect of the date and other information, the other party deeply felt it would lose the lawsuit, and withdrew the lawsuit in December, 2021. This case involves the accurate understanding and application of adjudication rules for IP malicious lawsuit and unfair competition.
In August 2021, CHOW LO FOOK Jewelry and its dealers filed a lawsuit against Zhou Liu Fu Jewelry with Shenzhen Luohu Court for dispute on infringement of reputation rights, arguing that Zhou Liu Fu Jeweler’s act of entrusting the law firm to send a lawyer's letter to its dealers, and the propaganda containing "boycott fake brands", "a store of HK CHOW LO FOOK Jewelry was fined 1.4 million yuan for infringement" and "HK CHOW LO FOOK Jeweler’s free ride of the popularity of the well-known brand Zhou Liu Fu Jewelry to confuse the public and was denounced by many parties and was deeply involved in a lawsuit" and other words infringed its reputation right. Unitalen lawyers provided evidence and reasoned in detail from various aspects. In the end, Shenzhen Luohu Court determined that Zhou Liu Fu Jeweler’s letter was within the reasonable scope of rights protection. The content of the propaganda was based on the content of the administrative penalty decision, civil ruling or civil judgment, and was not a fictitious or fabricated fact. Therefore, the behavior of Zhou Liu Fu Jewelry was not an insult or defamation, and did not constitute an infringement of the right of reputation. After the first-instance judgment was made, the other party filed an appeal and then withdrew.
In December 2021, CHOW LO FOOK Jewelry and its dealer Xindu District Di Zun Jewelry Store filed a discrediting dispute with Chengdu Intermediate Court against Zhou Liu Fu Jewelry and Jin Ai Jewelry Store, arguing that in July 2021, the dealer of Zhou Liu Fu Jewelry Jin Ai Jewelry Store broadcast on the LED screen of the storefront signboard "to believe the genuine Zhou Liu Fu here, and boycott the fake CHOW LO FOOK of a certain company in Hong Kong", and "no after-sales, no warranty, no notarization, self-employed", which constituted the discrediting. Unitalen lawyers, after careful research and judgment, formulated a counterclaim strategy, and filed a counterclaim in February 2022, accusing that CHOW LO FOOK Jewelry and its dealer Xindu District Di Zun Jewelry Store used "Boycott any fake brand Zhou Liu Fu without ? mark Authentic Hong Kong brand ? National authentication ? Trustworthy" and "I don't know what to do but giving some gifts. Zhou X Fu is not the official brand of HK CHOW LO FOOK Jewelry Int'l Group Limited. Please look for the brand endorsed by Cai Shaofen!" priorly in their promotional slogans in April 2021, which constituted the discrediting. The two parties engaged in a fierce confrontation in the court hearing around the four elements of discrediting, based on the evidences and facts. In the end, the court determined that the propaganda of Xindu District Di Zun Jewelry Store pointed to its competitor Zhou Liu Fu Jewelry, and the content it published was fabricated, disseminated false or misleading information, and the purpose of the propaganda was to spread the information that Jin Ai Jewelry Store sold products of unofficial "CHOW LO FOOK" brand, to make consumers have a bad impression and influenced their decision-making. The brand image and value of Zhou Liu Fu were damaged and degraded. Therefore, CHOW LO FOOK Jewelery's act of claiming that Zhou Liu Fu Jewelery was a "fake CHOW LO FOOK" constituted discrediting. In the judgment, the court confirmed that CHOW LO FOOK Jewelery and its multiple dealers infringed the exclusive rights of Zhou Liu Fu Jewelery's registered trademarks No. 7519198 and No. 13062591 for "Zhou Liu Fu" due to the irregular use of the trademark of Zhou Liu Fu. Thus, it is not without fact that Jin Ai jewelry store used the words "fake Zhou Liu Fu" in its promotional slogan to allege CHOW LO FOOK Jewelery. In this case, "self-employment" is a fact, "no notarization" does not refer to any specific practical meaning, and the propaganda slogan cannot produce any positive or negative effect. Nevertheless, the court still held that the advertisement of "no after-sales, no warranty" was misleading to some extent. Finally, the court comprehensively considered the actual situation of both parties and ruled that Xindu District Di Zun Jewelry Store shall compensate for the economic loss of Xindu District Jin Ai Jewelry Store.
Typical Significance:
This series of cases typically shows how the defendant can effectively defend or take the initiative in the case. The typical significance is mainly reflected in two aspects: on the one hand, the accurate understanding and application of the constituent elements of legal rules such as malicious lawsuit, unfair competition, reputation right infringement and discrediting; on the other hand, the reasonable formulation of litigation strategies, that is, how to take the initiative to use counterclaims in the accused cases to achieve the effect of reversing the positions of the host and the guest, thus winning in the confrontation of the case.
|
|
|
| |
| |
 Unitalen Represented Trademarks "后" and "the history of 后" of the Korean High-end Cosmetics Recognized as Well-known for the First Time in China by the Judicial System Unitalen Represented Trademarks "后" and "the history of 后" of the Korean High-end Cosmetics Recognized as Well-known for the First Time in China by the Judicial System
|

|
| |
|
|
Case brief:
The brand "WHOO后" (including trademarks " ", " ", " ", and " ", and " ", etc.) is a sub-brand of LG Household & Health Care Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "LG H&H"), which means the queen's secret. The WHOO后 brand was first launched in Korea in 2003, and then entered the Chinese market in 2005. As of 2016, cosmetics of the WHOO后 brand have nearly 200 off-line counters opened in 88 cities in China, and have official brand stores on-line in Tmall and JD.com. The product sales covered most provinces and cities in mainland China. With high-quality products and services, the brand has now become one of the top representative brands of Korean cosmetics in the world. ", etc.) is a sub-brand of LG Household & Health Care Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "LG H&H"), which means the queen's secret. The WHOO后 brand was first launched in Korea in 2003, and then entered the Chinese market in 2005. As of 2016, cosmetics of the WHOO后 brand have nearly 200 off-line counters opened in 88 cities in China, and have official brand stores on-line in Tmall and JD.com. The product sales covered most provinces and cities in mainland China. With high-quality products and services, the brand has now become one of the top representative brands of Korean cosmetics in the world.
LG H&H has two trademarks claimed in this case, including Trademark No. 4819575 " " (applied for registration in 2005 and approved for registration in 2009) and Trademark No. 9327294 " " (applied for registration in 2005 and approved for registration in 2009) and Trademark No. 9327294 " " (applied for registration in 2001 and approved for registration in 2012) approved for registration on goods of "Moisturizer Lotion; Cosmetics", etc. in class 3. " (applied for registration in 2001 and approved for registration in 2012) approved for registration on goods of "Moisturizer Lotion; Cosmetics", etc. in class 3.
In 2020, LG H&H found out that a Trading Limited Company in Shenzhen (hereinafter referred to as the "Shenzhen Company") used trademarks "The History of Whoo一后", "The History of Whoo后", "Whoo一后" and "Whoo 后", etc. on the website www.whoo.com, Sina Weibo account "Whoo后", etc. to promote funeral goods and services such as shrouds, wreaths, coffins, cremation urns and the like, and declared to "commit to build the best funeral etiquette and supplies brand Whoo一后 in China". Not only that, since May 2016, the Shenzhen Company has also applied for registration of trademarks "Whoo后", "Whoo一后", and " ", etc. in the classes related to funeral supplies and funeral services of classes 20, 24, 26, 44, and 45, and the trademarks have been approved for registration. The earliest applied trademarks had been announced invalid by the China National Intellectual Property Administration before the first-instance judgment was made; the trademark " ", etc. in the classes related to funeral supplies and funeral services of classes 20, 24, 26, 44, and 45, and the trademarks have been approved for registration. The earliest applied trademarks had been announced invalid by the China National Intellectual Property Administration before the first-instance judgment was made; the trademark " " applied for registration on goods of "Cosmetic utensils" etc. in class 21 was rejected. The legal representative of the Shenzhen Company had expressed the willingness to sell the approved and registered trademarks related to "Whoo后" and the domain name "whoo.com" at a price of 2.5 million US dollars. " applied for registration on goods of "Cosmetic utensils" etc. in class 21 was rejected. The legal representative of the Shenzhen Company had expressed the willingness to sell the approved and registered trademarks related to "Whoo后" and the domain name "whoo.com" at a price of 2.5 million US dollars.
In 2021, LG H&H filed a trademark infringement lawsuit against the Shenzhen Company with the Shenzhen Intermediate People's Court. After hearing, the Shenzhen Intermediate People's Court supported the claims of LG H&H in ceasing the infringement and eliminating the impact, and awarded compensatory damages in the amount of RMB 450,000 yuan (LG H&H claimed 500,000 yuan). This case is currently in the appeal period.
Determination of the Court:
First, regarding the necessity of being recognized as well-known. The court held that, in this case, the goods and services on which the accused trademarks of the Shenzhen Company are used and the goods on which the trademarks claimed by LG H&H are approved for use are not the same or similar goods and services, which involves the issue of cross-class protection. Therefore, it is necessary for the trademarks to be recognized as well-known in this case.
Second, regarding the possibility of being recognized as well-known. The court held that the evidence in this case could prove that the products of the two claimed trademarks that have been continuously used have huge market influence in terms of market share, sales area, publicity and promotion, etc. and have high brand value, and determined that before the Shenzhen Company applied for registration of trademarks related to "Whoo后", Trademark No. 4819575 " " and Trademark No. 9327294 " " and Trademark No. 9327294 " 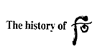 " have achieved the well-known state on goods of cosmetics in class 3, and the well-known state has maintained until the alleged act was evidenced and prosecuted. " have achieved the well-known state on goods of cosmetics in class 3, and the well-known state has maintained until the alleged act was evidenced and prosecuted.
Third, regarding determining the trademark infringement. The court held that in actual use and publicity, "whoo" and trademark "  " and trademark "Whoo 后" often appeared together, and "Whoo" itself is a transliteration of "后". The above trademarks, upon extensive and long-term publicity and use, have formed and continuously deepened the corresponding relationship. The accused trademarks "Whoo一后", "Whoo 后", "The History of Whoo一后" and "The History of Whoo后" constitute reproduction, imitation and translation of the trademarks " " and trademark "Whoo 后" often appeared together, and "Whoo" itself is a transliteration of "后". The above trademarks, upon extensive and long-term publicity and use, have formed and continuously deepened the corresponding relationship. The accused trademarks "Whoo一后", "Whoo 后", "The History of Whoo一后" and "The History of Whoo后" constitute reproduction, imitation and translation of the trademarks "  " and " " and "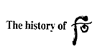 ", respectively. Considering the strong distinctiveness and high notability of the trademarks claimed in this case, the relevant public will mistake that the accused trademarks are considerably related to the well-known trademarks of LG H&H involved in this case, which will damage the interests of the trademark registrant. Therefore, the court found that the trademark infringement was established. ", respectively. Considering the strong distinctiveness and high notability of the trademarks claimed in this case, the relevant public will mistake that the accused trademarks are considerably related to the well-known trademarks of LG H&H involved in this case, which will damage the interests of the trademark registrant. Therefore, the court found that the trademark infringement was established.
Fourth, regarding determining the amount of compensation. The economic losses and reasonable expenses claimed by LG H&H amounted to 500,000 yuan. The court has comprehensively considered factors such as the notability of the trademarks claimed, the circumstances and nature of the alleged infringement act, the reasonable expenses of LG H&H, and the infringement intent of the Shenzhen Company, and determined the economic losses and reasonable right protection costs totaling 450,000 yuan as appropriate.
Typical Significance:
This case not only protects the legitimate rights and interests of LG H&H and protects the brand reputation of WHOO后, but also defeats the malicious infringement act of clinging to the notability of others' trademarks and downplaying and defaming the well-known trademarks. After the " " and " " and "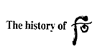 " trademarks were recognized as well-known trademarks for the first time in China, it is believed that in the future, right protection of the WHOO后 brand of LG H&H in China will be unhindered. " trademarks were recognized as well-known trademarks for the first time in China, it is believed that in the future, right protection of the WHOO后 brand of LG H&H in China will be unhindered.
|
|
|
| |
| |
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| Unitalen News
|
 |
| |
|
|
 Unitalen Received the "China-Japan Trademark Exchange Contribution Award" Unitalen Received the "China-Japan Trademark Exchange Contribution Award"
|

|
| |
| |
|
2022 marks the 20th anniversary of the signing of the cooperation agreement between the China Trademark Association (CTA) and the Japan Patent Attorneys Association (JPAA). CTA and JPAA together carried out the selection of the "China-Japan Trademark Exchange Contribution Award". Unitalen Attorneys at Law has won this honor for its outstanding performance, remarkable exchange contribution and excellent influence in the field of Chinese and Japanese trademarks.
|
|
|
| |
| |
 Unitalen Xi'an Branch and School of Occidental Studies in XISU Jointly Build a Talent Training Base Unitalen Xi'an Branch and School of Occidental Studies in XISU Jointly Build a Talent Training Base
|

|
| |
| |
|
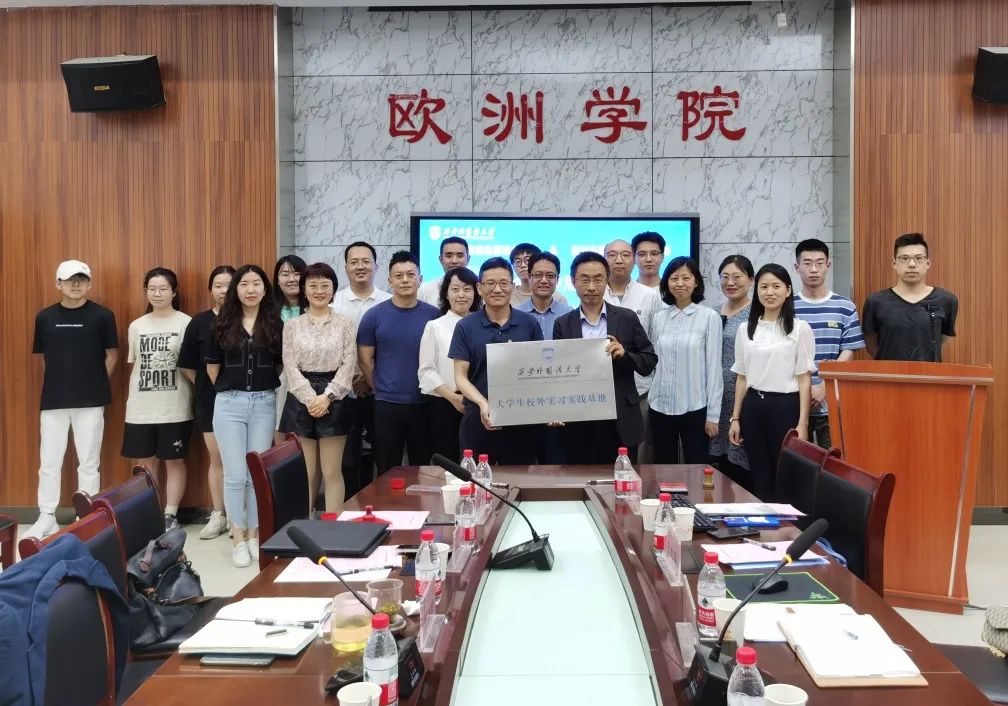
To actively expand the new mechanism of school-enterprise cooperation and explore new models of talent training, on the afternoon of May 20, 2022, Xi'an Branch of Unitalen Attorneys at Law and the School of Occidental Studies of Xi'an International Studies University (XISU) held a school-enterprise cooperation negotiation and off-campus internship and practice base signing and licensing ceremony.

|
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
| Unitalen Insights
|
 |
| |
|
|
 Coping with and Countering against IP-related Malicious Proceedings Coping with and Countering against IP-related Malicious Proceedings
|

|
| |
| |
|
With the increasing protection effort on intellectual property and the increasing amount of compensation for infringement in China, malicious proceedings filed with respect to intellectual property gradually emerge in the IP field. Recently, the Supreme People's Court issued the "Official Reply on Issues concerning the Claim of the Defendant for Compensation for Reasonable Expenses on the Ground that the Plaintiff Abuses Rights in the Action of Intellectual Property Infringement" (hereinafter referred to as the "Official Reply on the Claim for Compensation for Reasonable Expenses on the Ground of Rights Abuses" or the "Official Reply"). The Third Civil Tribunal of the Supreme People's Court has also issued an understanding and application of the Official Reply recently. In combination with the Official Reply of the Supreme People's Court and its understanding and application, as well as the "一品石" (Yipinshi)" case represented by Unitalen, coping with and countering against IP-related malicious proceedings will be introduced briefly here.
I. Identification of abuse of intellectual property rights and malicious proceedings
1. What is "malicious proceedings"?
Malicious proceedings essentially is an abuse of the procedural rights, and is contrary to the provision of Article 13 of the Civil Procedure Law that "in civil procedures, the principle of good faith shall be adhered to". In judicial practice, malicious proceedings is generally manifested as abuse of rights (flawed foundation of rights), fabricating facts to prosecute, malicious preservation, multiplicity of actions, etc.
According to the Guiding Opinions of the High People's Court of Jiangsu Province on Implementing the Strictest Judicial Protection on Intellectual Property and Providing Judicial Guarantee for High-quality Development, where an actor knows that the intellectual property rights he/she has acquired are not substantively legitimate, but based on the intellectual property rights he/she enjoys in form, for the purpose of unfair competition and hindering the normal operation of the opposite party, he/she initiates intellectual property proceedings against others and causes damage to others, it is a malicious proceedings of intellectual property.
2. The "four elements" of constituting malicious proceedings of intellectual property in judicial practice.
1) One party makes a certain request by filing an intellectual property proceedings, or threatens to make a certain request (abandoning claims, withdrawing lawsuits).
2) The party making the request knows that he/she has no legal and factual basis and has subjective malice. "Malice" is mainly reflected in firstly knowing that his/her claims lack factual and legal basis, and secondly having an improper purpose of proceedings that infringes upon the legitimate rights and interests of the other party.
3) There are actual damage consequences (property damage, loss of reputation).
4) There is a causal relationship between the act of filing of an intellectual property proceeding by the one party making the request and the resulting damage consequences.
II. A brief interpretation on the "Official Reply on the Claim for Compensation for Reasonable Expenses on the Ground of Rights Abuses" of the Supreme People's Court.
In the previously existing laws and judicial practice in China, only the defeated defendant bears reasonable expenses such as the attorney fees of the prevailing plaintiff, and if the prevailing defendant intends to claim that the defeated plaintiff compensates for the reasonable expenses that the defendant has paid, the defendant can only file a lawsuit separately. The "Official Reply on the Claim for Compensation for Reasonable Expenses on the Ground of Rights Abuses" of the Supreme People's Court benchmarks against the international treaties (the RCEP agreement stipulates that "the defeated party pays reasonable attorney fees and other fees to the prevailing party", and does not limit the status of the subject of the lawsuit, that is, the defeated party and the prevailing party are not corresponding to the plaintiff and the defendant), and solves the problem of "one-way compensation".
1. Applicable conditions:
The defendant bears the burden of proof (the plaintiff filling a lawsuit is an abuse of rights; the defendant's legitimate rights and interests are damaged due to the lawsuit filed by the plaintiff).
The plaintiff filling a lawsuit constitutes an abuse of rights stipulated by laws (abuse of rights vs malicious proceedings; it is only a procedural provision, and the constituent elements have to be judged according to the review standards for the entity of abusing rights in the General Provisions of the Civil Code).
The plaintiff compensates the defendant for the reasonable expenses incurred from the proceedings (attorney fees, transportation fees, room and board expenses, etc., excluding other economic losses caused by the abuse of the procedural rights, which should be resolved through other ways).
2. Ways of application:
1) The claim is made in accordance with the law by means of counterclaim. There is a causal relationship between the claims made based on that the prevailing defendant claims that the plaintiff that abuses rights shall bear the reasonable expenses incurred from the lawsuit and the plaintiff's lawsuit against the defendant for infringement, and the cases should be consolidated for hearing. For example, in the "一品石" (yipinshi) trademark case, in the accused case, it is claimed for defense that the plaintiff's rights were acquired maliciously and the rights were abused. 2) By making the request by means of a separate lawsuit, a separate lawsuit may be filed for the liability dispute regarding the damages caused by the malicious intellectual property proceedings, claiming reasonable expenses such as attorney fees. For instance, in the copyright case of "一品石" (yipinshi), an unfair competition lawsuit/infringement lawsuit was initiated, and the malicious warnings, malicious complaints and malicious lawsuit act of the trademark registrant are held accountable together. Or after the accused infringement case prevails, a lawsuit may be separately filed for counter-compensation against the malicious lawsuit (for the liability dispute regarding the damages caused by the malicious intellectual property proceedings), claiming compensation for the reasonable expenses.
3) Applicable spaces are reserved for other means, and the expression "requesting according to law" reserves spaces for exploration for the application of other means than counterclaims and separate lawsuits. For example, in the case of receiving complaints or warnings, a lawsuit for confirmation of non-infringement may be initiated, and through procedures such as invalidation/revocation, the foundation of rights may be moved.
III. Coping Strategy against Malicious Proceedings/Right Abuse
1. For the defendant, it may be claimed for defense that the plaintiff's rights were acquired maliciously, which constitutes abuse of rights. In addition to the above "一品石" (yipinshi) case represented by Unitalen, the "ELLASSAY" case, the guiding case No. 82 of the Supreme Court, the "SAIKESI" case in the Annual Report on IP Cases (2015) issued by the Supreme People's Court, and the "Uniqlo" case in the top 10 IP cases in Chinese courts in 2018 are all typical cases of this type.
2. In the case of receiving administrative complaints or warnings, a lawsuit for declaration of non-infringement may be initiated. The "WeChat Pay" case and others represented by Unitalen are typical cases of this type.
3. After the accused prevails in an infringement case, a lawsuit may be separately filed for counter-compensation against the malicious lawsuit (for the liability dispute of damages caused by the malicious intellectual property proceedings), claiming compensation for the reasonable expenses. The top 10 IP cases in Chinese courts in 2019 and the "金蝶妙想" (jindiemiaoxiang) case and others represented by Unitalen are typical cases of this type.
4. An unfair competition lawsuit/infringement lawsuit (such as the copyright case of "一品石" (yipinshi)) may be initiated, and the malicious warnings, malicious complaints and malicious lawsuits of the trademark registrant may be held accountable together.
5. In addition, through procedures such as invalidation/revocation against the "trademarks claimed" by the plaintiff, the foundation of rights may be moved. The "Zirkulin" case and others represented by Unitalen are typical cases of this type.
|
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
